What other treatments your child has had ;Atypical clubfeet or complex idiopathic clubfeet are defined by Ponseti as "having rigid equinus, severe plantar flexion of all metatarsals, a deep crease above the heel, a transverse crease in the sole of the foot, and a short hyperextended first toe" (Ponseti, 06) While typical idiopathic clubfeet respond well to the standard method of Ponseti casting and generally correct after 46 casts, atypical clubfeet are resistant to correction and standard manipulation and casting may leadClubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inward and downward The affected foot and leg may be smaller in size compared to the other Approximately 50% of cases of clubfoot affect both feet Most of the time, it is not associated with other problems Without treatment, the foot remains deformed, and people walk on the sides of their feet

Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram
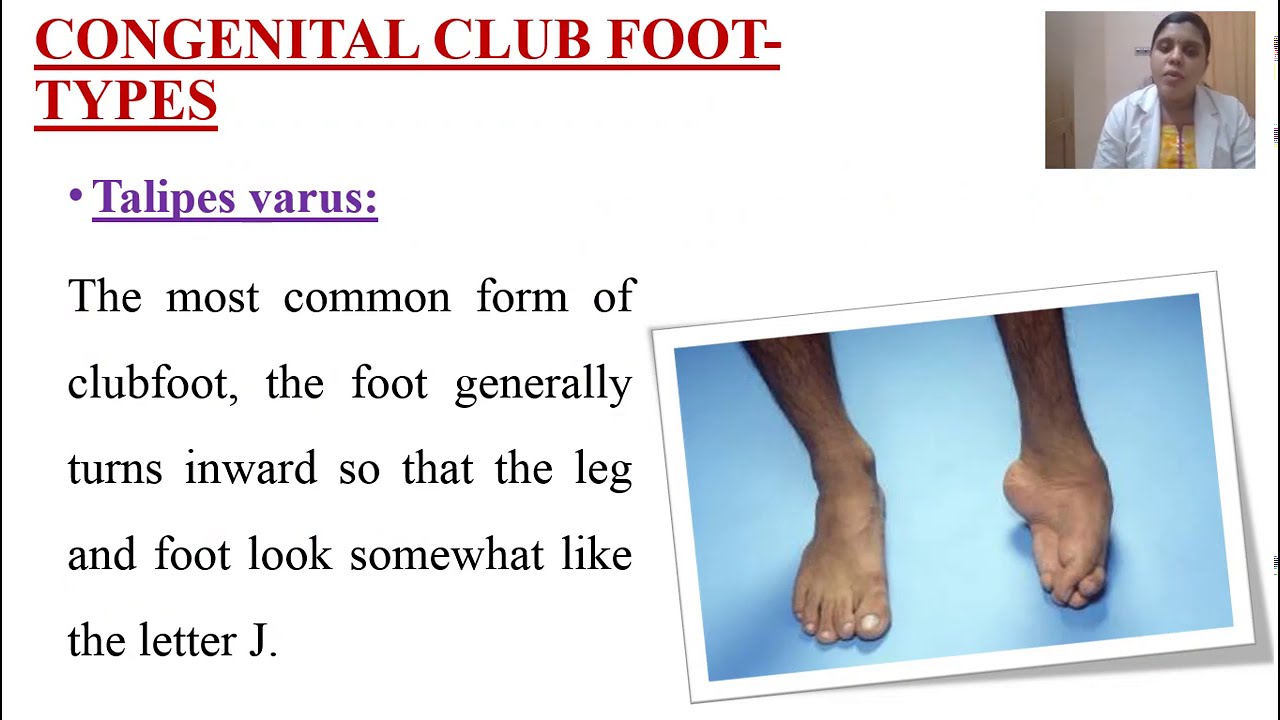
Congenital clubfoot types
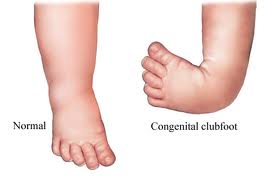
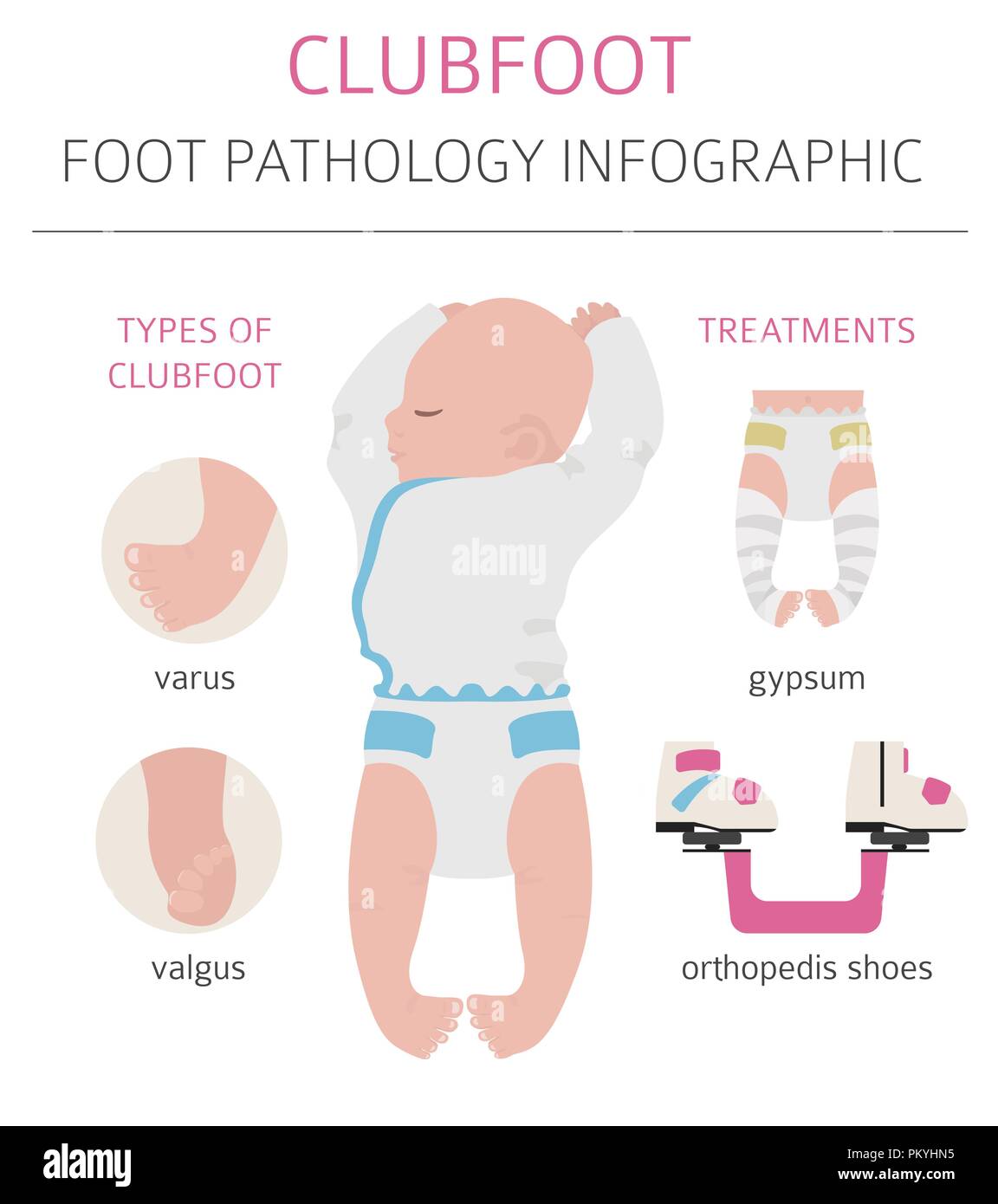
Congenital clubfoot types-They include A foot that turns inward and downward, with toes pointing toward the opposite foot The clubfoot may be smaller than the other foot (up to ½ inch shorter) The heel on the clubfoot may be smaller than normal In severe cases, the clubfoot may be twisted upside downThere are actually different types of clubfoot, but the following are the typical foot deformities that are associated with the condition Plantarflexion – the ankle is twisted downward Cavus foot – the foot arch is unusually high Varus – the heel assumes the position of inversion, which draws the forefoot inward as well


Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
Clubfoot is a birth defect that makes one or both of a baby's feet point down and turn in Most clubfeet can be successfully corrected using the nonsurgical Ponseti methodA clubfoot is a congenital deformity in which the affected foot appears rotated internally at the ankle It is treatable in many casesThere are two types of clubfoot Isolated or idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type If your child has clubfoot with no other medical problems, it's called isolated clubfoot Idiopathic means that the cause of clubfoot is not known
Clubfoot is a fairly common birth defect in which the foot is twisted in and down In about half of people with club foot, both feet are affected Although club foot can be treated with stretching exercises, casts, braces, or surgery, there is no cure Club foot sufferers may experience limited motion and pain years after "successful" treatmentThese can increase the risk of clubfoot as well 13 TYPES Talipus varus inversion or bending inward of foot Talipes valgus eversion or bending outward of foot Talipes equinus planter flexion and toe is lowe than heel • Talipes calcaneous dorsiflexion, toe is higher than heelClubfoot is often broadly classified into two major groups Isolated (idiopathic) clubfoot is the most common form of the deformity and occurs in children who have no other medical problems Nonisolated clubfoot occurs in combination with various health conditions or neuromuscular disorders, such as arthrogryposis and spina bifida
And intrinsic (rigid) type, where manual reduction is impossible TheWhile some use CTEV and clubfoot (CF) synonymously, in certain publications term clubfoot is considered a more general descriptive term that describes three distinct abnormalities talipes equinovarus (adduction of the forefoot, inversion of the heel and plantar flexion of the forefoot and ankle)Clubfoot is a deformity of the whole foot that is present at birth There are several types of clubfoot that are jointly known as 'talipes', as the deformity is mostly in the talus (a bone in the ankle) The most common of the talipes is what is known as "talipes equino varus" it is so common that the word clubfoot is commonly used to refer to this



55 Talipes Ideas Club Foot Club Foot Baby Feet



Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
"The real challenge of the Ponseti Method begins when casting ends Children must wear a brace locking their feet in place 23 hours a day After three months, the time required begins to drop incrementally until age 4 or 5 when, according to Dr Ponseti, the gene that causes club feet is no longer active" Braces Read More »It has four classification Equius, midfoot cavus, forefoot adduction and hind foot varus When left untreated, children having clubfoot walk on the sides and/or top of their feet, which leads to callus formation, skin and bone infections, substantial limitation in mobility, reduced employment opportunities and inability to wear standard shoesComplex Clubfoot any foot with deformity that has received any type of treatment other than the Ponseti method may have added complexity because of additional pathology or scarring from surgery Resistant Clubfoot this is a clubfoot where Ponseti treatment has been correctly performed but there has been no significant improvement It is often found that this type of clubfoot is not in fact idiopathic after all and is secondary or syndromic


Club Foot Nhs


Club Foot
Clubfoot is often broadly classified into two major groups Isolated (idiopathic) clubfoot is the most common form of the deformity and occurs in children who have no other medical problems Nonisolated clubfoot occurs in combination with various health conditions or neuromuscular disorders, such as arthrogryposis and spina bifidaClubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Idiopathic Clubfoot Also known as talipes equinovarus, idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type of clubfoot and is present at birthClubfoot Doctors use the term "clubfoot" to describe a range of foot abnormalities usually present at birth (congenital) In most cases, the front of the foot is twisted downward and inward, the arch is increased, and the heel is turned inward



4 1 Clubfoot Types Clubfoot Guide 123


Clubfoot High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
Clubfoot can be repaired by casting or surgery Casting Sometimes nonsurgical treatments, such as casting, can correct clubfoot Casting is a method for correcting clubfoot in the hopes ofThere are two main types of congenital clubfoot idiopathic (80% of cases) and secondary clubfoot (% of cases) The idiopathic congenital clubfoot is a multifactorial condition that includes environmental, vascular, positional, and genetic factors Clubfoot has a tendency to segregate in families the risk of developing congenitalClubfoot is a common defect present at birth and occurs in every 1,000 live births Bilateral TEV can be found be found in nearly 50% of cases Bilateral TEV can be found be found in nearly 50% of cases



Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar
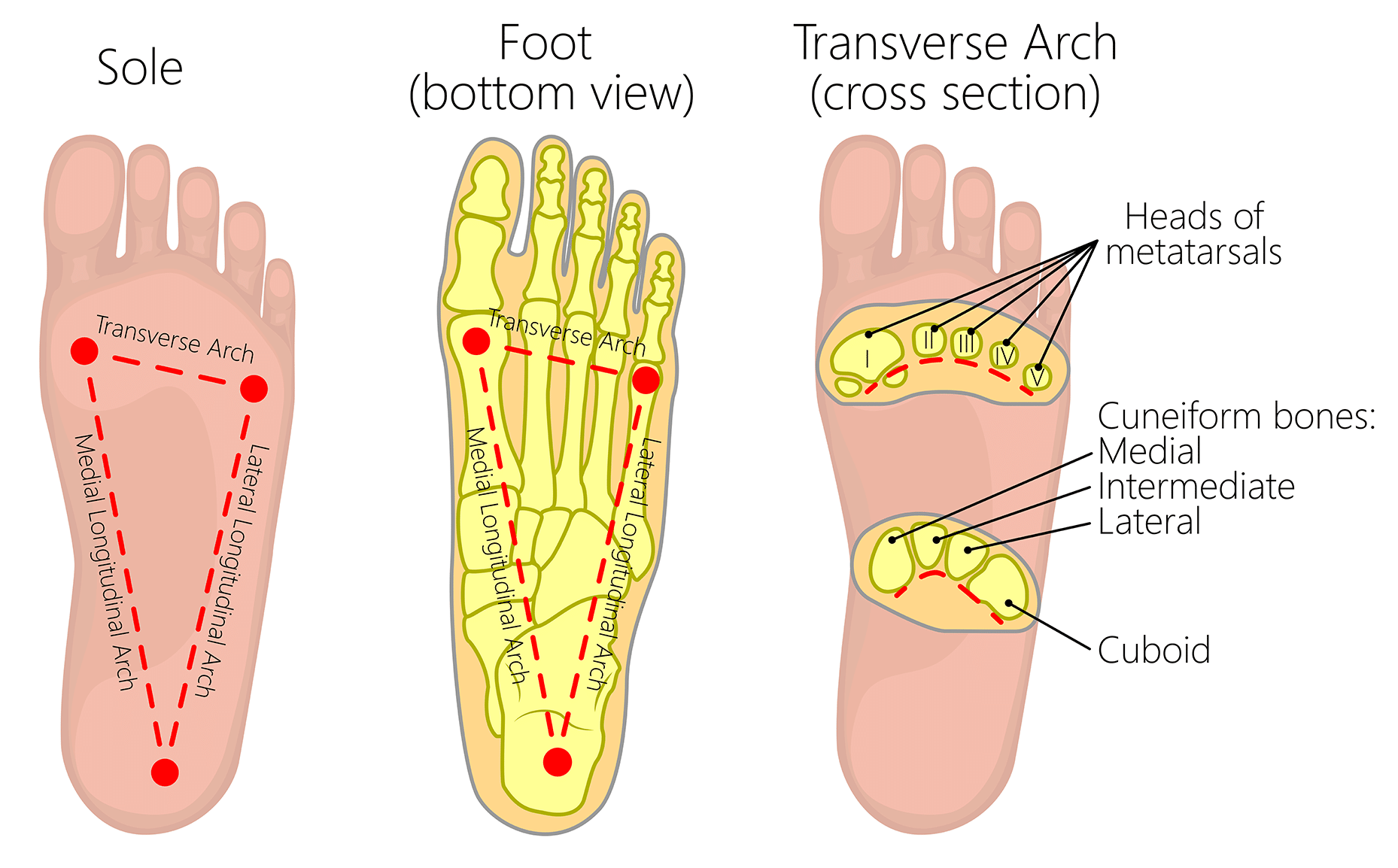


The Arches Of The Foot Longitudinal Transverse Teachmeanatomy
Types of Clubfoot including their causes, diagnosis, and related symptoms from a list of 386 total causes of symptom ClubfootClubfoot can be classified into extrinsic (supple) type, which is essentially a severe positional or soft tissue deformity;Clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus, is the most common pediatric orthopedic deformity requiring treatment Although the deformity may appear to be severe, particularly when first discovered after



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
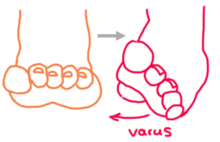


Clubfoot Wikipedia
Types Dr Mallon Nyati, a consultant in orthopaedics surgery at Mulago National Referral Hospital, says there are various types of clubfoot with congenital being the most common serious birth defect He notes that in 08, it was discovered that more than 1,500 children are born with clubfoot in Uganda each yearClubfoot can be classified into extrinsic (supple) type, which is essentially a severe positional or soft tissue deformity;Grade 2 has a hoof angle of 58 degrees greater, and the heel will not touch the ground when trimmed to normal length Grade 3 club foot has an anterior hoof wall described as dished with the heel twice as wide as the toe Grade 4 exhibits a heavily dished hoof wall with an angle of 80 degrees or more Top



Club Foot



Club Foot
There are two types of clubfoot Isolated or idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type If your child has clubfoot with no other medical problems, it's called isolated clubfoot Idiopathic means that the cause of clubfoot is not knownTypes of Clubfoot There are three types of clubfoot that your child can be diagnosed with Idiopathic Clubfoot A true (idiopathic) clubfoot accounts for the vast majority of cases This type is stiff or rigid, and very hard to manipulate Positional ClubfootMost commonly, it is classified as "Idiopathic Clubfoot" which means there is no known cause "Secondary Clubfoot" which occurs when there is another disease or condition that is causing or is linked to the clubfoot, such conditions are usually neurological or syndromic disorders such as Arthrogyposis or Spina Bifida



Clubfoot Wikipedia
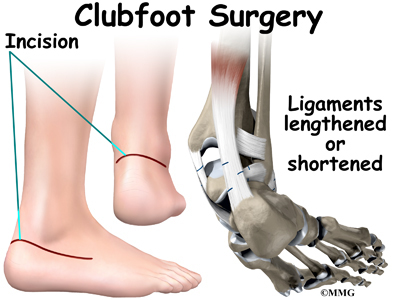


Clubfoot Eorthopod Com
Types of clubfoot (not all clubfeet are the same) •Untreated •Treated •Resistant •Recurrent •Neglected •ComplexDiagnosis Most commonly, a doctor recognizes clubfoot soon after birth just from looking at the shape and positioning of the newborn's foot Occasionally, the doctor may request Xrays to fully understand how severe the clubfoot is, but usually Xrays are not necessaryClubfoot is a fairly common birth defect in which the foot is twisted in and down In about half of people with club foot, both feet are affected Although club foot can be treated with stretching exercises, casts, braces, or surgery, there is no cure Club foot sufferers may experience limited motion and pain years after "successful" treatment



Clubfoot Treatment In India Dr Nargesh Agrawal
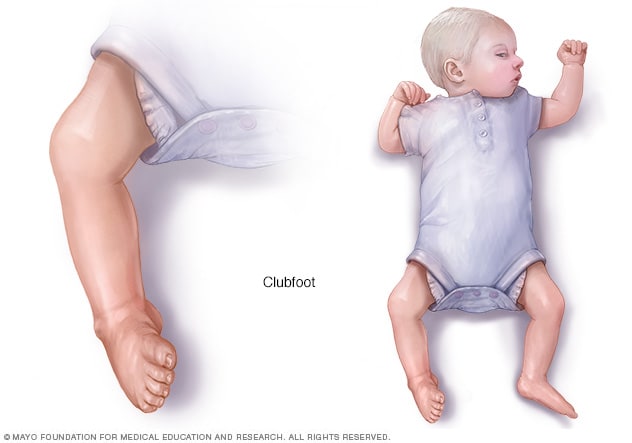


Clubfoot Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Other experts are of the opinion that either nerve or muscle problems in the lower leg cause the foot, or feet, to be turned in Clubfeet are sometimes associated with other conditions such as spina bifida or arthrogryposis Patients with arthrogryposis may have a more severe form of clubfootClubfoot can be repaired by casting or surgery Casting Sometimes nonsurgical treatments, such as casting, can correct clubfoot Casting is a method for correcting clubfoot in the hopes ofMost tarsal coalitions may be classified as one of two types a calcaneonavicular coalition, in which the tissue develops between the calcaneus (heel bone) and the navicular (one of the foot bones), or a talocalcaneal or subtalar coalition, in which the coalition develops between the calcaneus and the talus (the ankle bone)
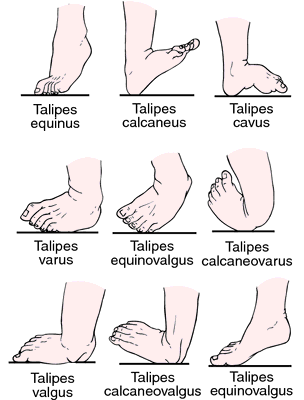


Talipes Definition Of Talipes By Medical Dictionary



Club Foot Foot Musculoskeletal System
The type of surgery that is done depends on How serious the clubfoot is;Talipes equinovarus Incidence Clubfoot is a common defect present at birth and occurs in every 1,000 live births Bilateral TEV can be found be found in nearly 50% of cases About twice as many males are born with the congenital form than females Talipes equinovarus TypesClubfoot is a deformity of the whole foot that is present at birth There are several types of clubfoot that are jointly known as 'talipes', as the deformity is mostly in the talus (a bone in the ankle) The most common of the talipes is what is known as "talipes equino varus" it is so common that the word clubfoot is commonly used to refer to this
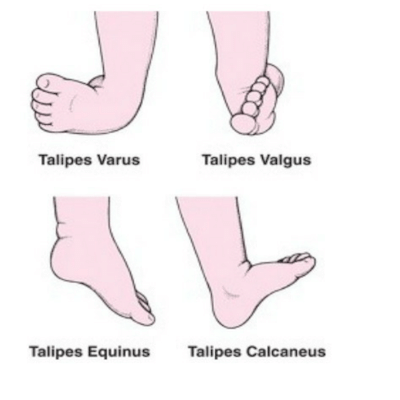


Club Foot Shoes Ponseti Denis Brown Dobs Bar Gm Medical Kenya
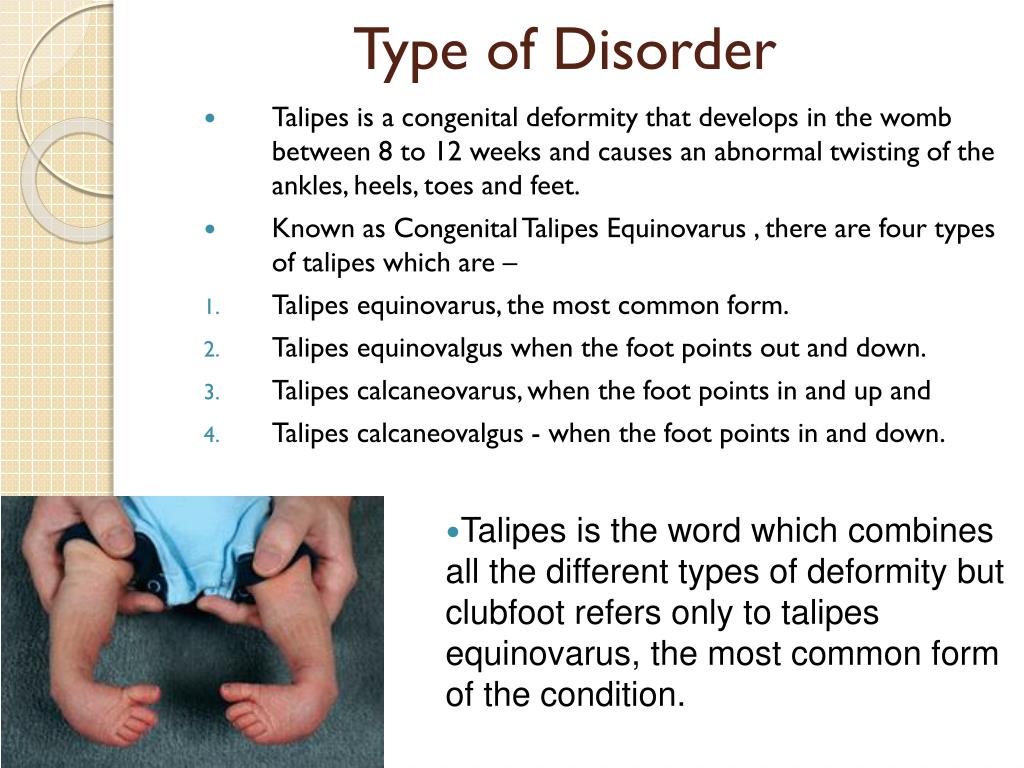


Ppt Club Foot Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Your child will have general anesthesia (asleep and painfree) during the surgery Ligaments are tissues that help hold the bones together in the body Tendons are tissues that help attach muscles to bonesThere are two types of clubfoot Isolated clubfoot (also called idiopathic clubfoot) This is the most common type It happens in children who have no other medical problems Nonisolated clubfoot This type happens together with other health problems, like arthrogryposis or spina bifida A baby with arthrogryposis is born with joint problems that make it hard for him to move his hands or legsThere are two main types of congenital clubfoot idiopathic (80% of cases) and secondary clubfoot (% of cases) The idiopathic congenital clubfoot is a multifactorial condition that includes environmental, vascular, positional, and genetic factors Clubfoot has a tendency to segregate in families the risk of developing congenital



Clubfoot Hd Stock Images Shutterstock



Greatly Blessed Clubfoot Basics Life With An Afo Club Foot Baby China Adoption Baby Time
Other experts are of the opinion that either nerve or muscle problems in the lower leg cause the foot, or feet, to be turned in Clubfeet are sometimes associated with other conditions such as spina bifida or arthrogryposis Patients with arthrogryposis may have a more severe form of clubfootThe Achilles tendon and posterior ankle are contracted, and the foot is inverted and rotated in relationship to the leg If left untreated, weight bearing would be on the outside of the foot Clubfoot is seen more in males than females and occurs most commonly in just one, not both feetThere are two main types of congenital clubfoot idiopathic (80% of cases) and secondary clubfoot (% of cases) The idiopathic congenital clubfoot is a multifactorial condition that includes environmental, vascular, positional, and genetic factors Clubfoot has a tendency to segregate in families the risk of developing congenital



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine



Club Foot Telipes Biology Zoology Facebook
While some use CTEV and clubfoot (CF) synonymously, in certain publications term clubfoot is considered a more general descriptive term that describes three distinct abnormalities talipes equinovarus (adduction of the forefoot, inversion of the heel and plantar flexion of the forefoot and ankle)And intrinsic (rigid) type, where manual reduction is impossible TheClubfoot is a birth defect that makes one or both of a baby's feet point down and turn in Most clubfeet can be successfully corrected using the nonsurgical Ponseti method



Honourable Ram Nath Kovind Inaugurates Global Clubfoot Conference Virily



Talipes Equinovarus Flashcards Quizlet
There are two types of clubfoot Isolated or idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type If your child has clubfoot with no other medical problems, it's called isolated clubfoot Idiopathic means that the cause of clubfoot is not knownClubfoot is a birth defect that makes one or both of a baby's feet point down and turn in Most clubfeet can be successfully corrected using the nonsurgical Ponseti method


Club Foot Interactive Health



Walking Gait Abnormalities Boston Children S Hospital



Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets



Foot Deformities Various Talipes Conditions Pediatric Physical Therapy Pediatric Nursing Sensory Therapy
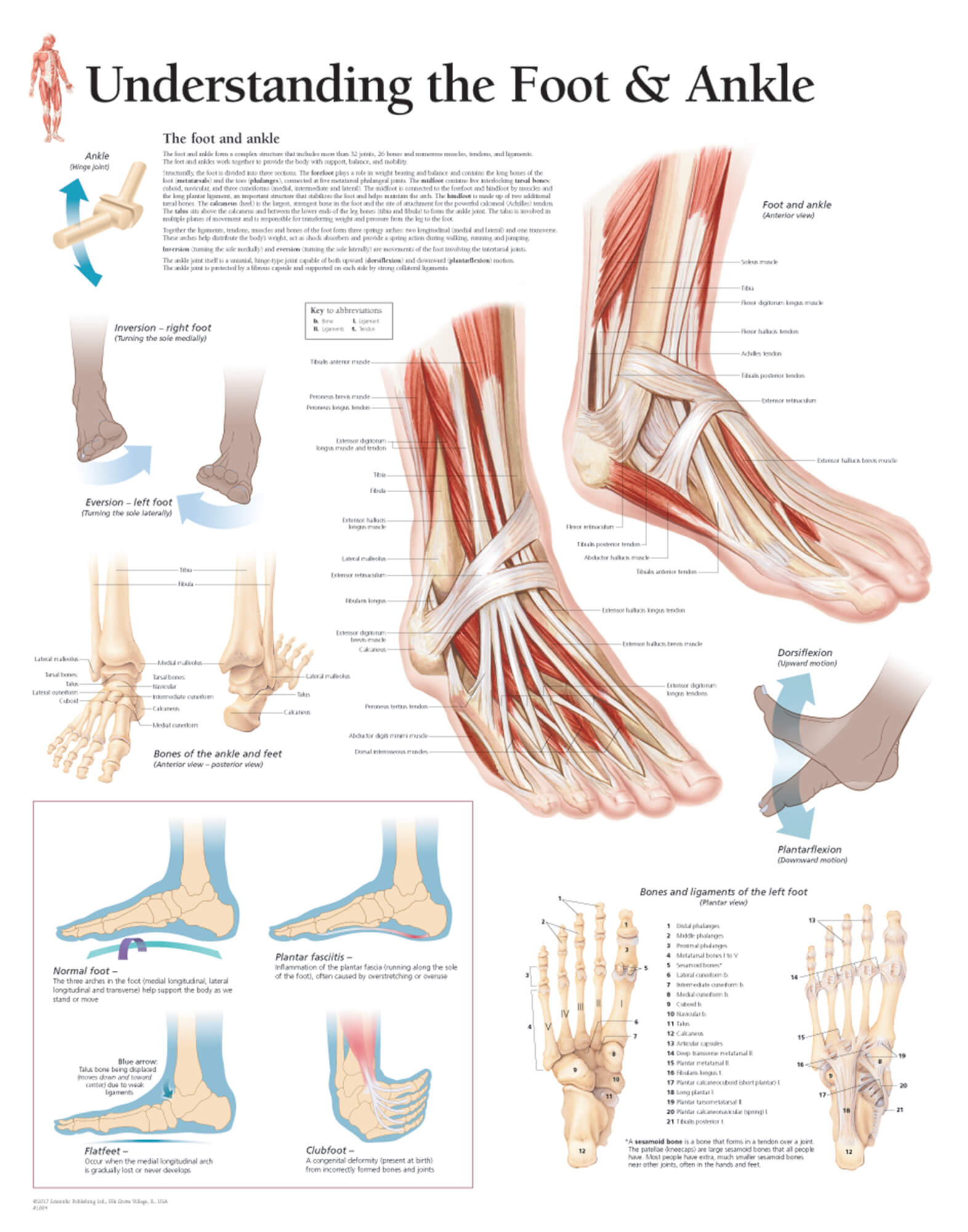


Understanding The Foot Ankle Scientific Publishing



4 1 Clubfoot Types Clubfoot Guide 123


Congenital Club Foot In Child Kerala Nurses Hub Youtube



Club Foot Talipes In Babies Causes Signs Treatment Youtube



Talipes Equinovarus Pictures Club Foot Closeup Of A Newborn Also Called Talipes



Talipes Babycentre Uk



Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus The Nepali Doctor



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com


Pediatric Foot Deformities An Overview



Orthokids Vertical Talus



Ctev Congenital Club Foot



Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Club Foot Symptoms And Treatment



Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital



Club Foot Horse Anatomy Horse Care Horses And Dogs



Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram



Club Foot Ctev Instanursing Online Facebook



Clubfoot Hd Stock Images Shutterstock



Clubfoot Wikipedia



Clubfoot Treatment In Iran Best Doctors Clinics Free Consultation



Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar



The 17 Abjs Nicolas Andry Award Advancing Personalized Medicine For Clubfoot Through Translational Research Springerlink


Clubfoot Stock Illustrations 74 Clubfoot Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime


Tibial Hemimelia International Center For Limb Lengthening



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments
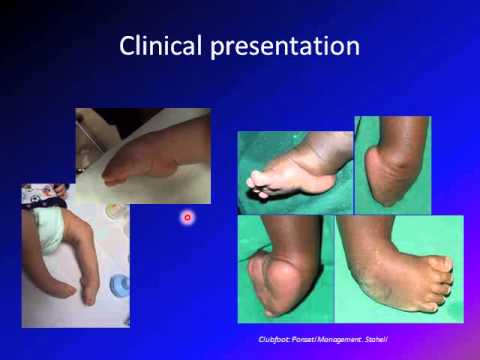


Clubfoot Talipes Equinovarus Tev Youtube



Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram
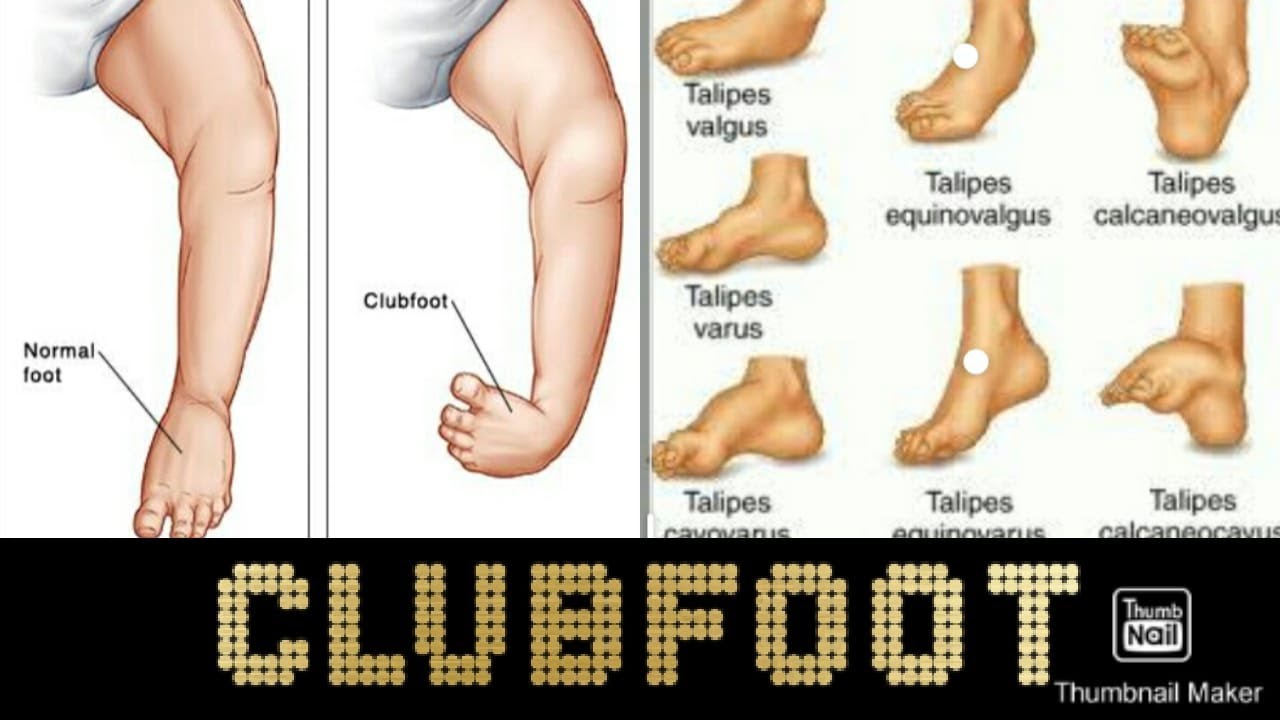


Clubfoot Its Types And Causes Simplified In Hindi Youtube



Clubfoot Repair Treatments Procedure Outlook


Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
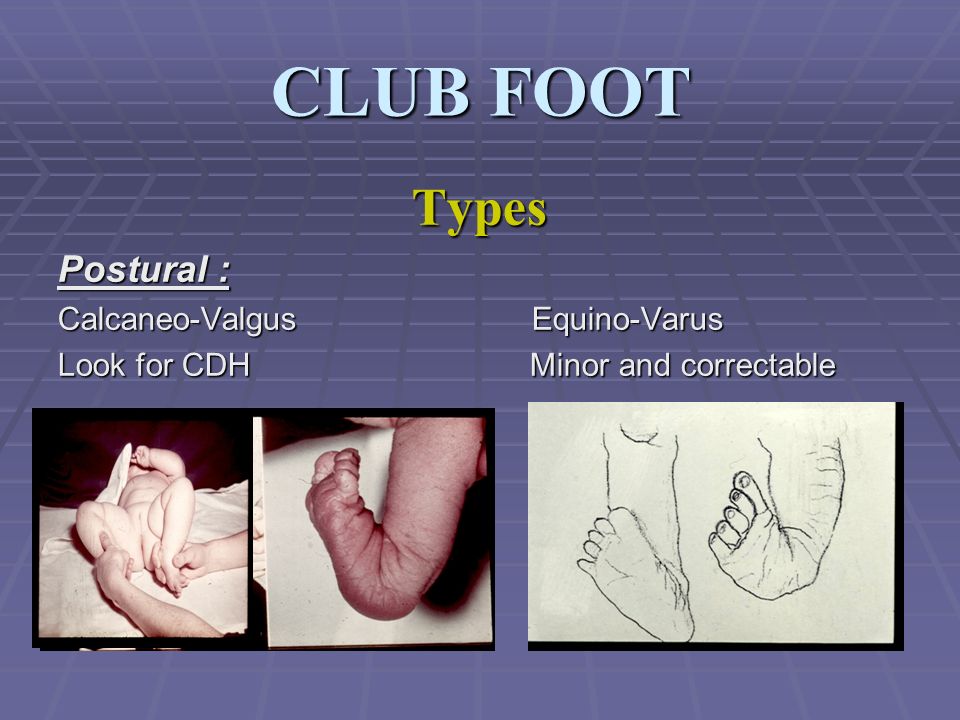


Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Congenital Clubfoot Ppt Video Online Download


Clubfoot In Children An Overview The Foot And Ankle Online Journal



Toenail Problems Causes Symptoms And Treatments
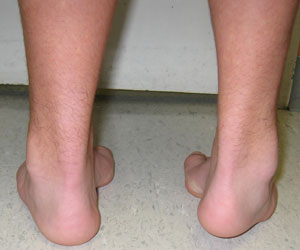


Pediatric Foot Deformities An Overview



Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital
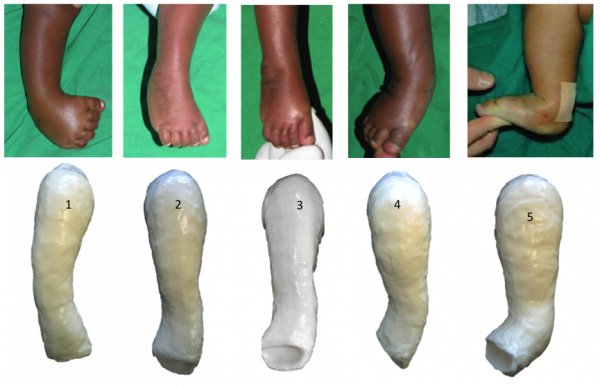


Ponseti Method Physiopedia



Clubfoot Wikipedia



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments



Club Foot Kids Time Out Dubai
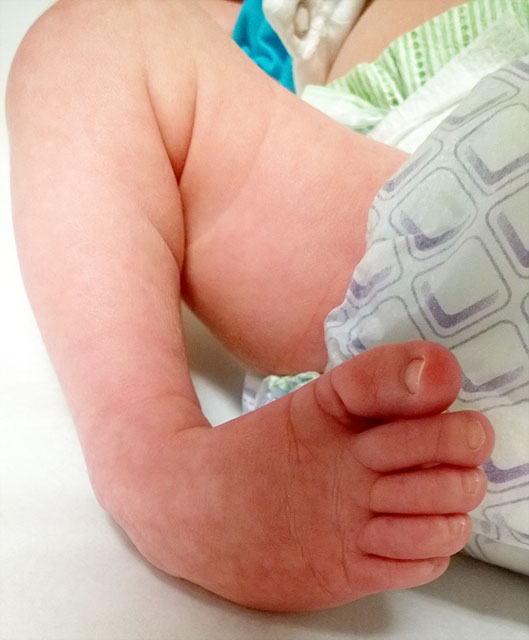


Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine



Clubfoot Types Archives Tebmedtourism


Clubfoot Orthoinfo os
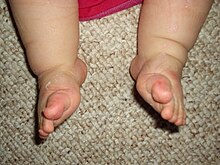


Clubfoot Wikipedia



Best Club Foot Shoes Models For Pes Equinovarus Treatment


Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre



The Newborn Foot American Family Physician



Clubfoot Archives African Journal Of Current Medical Research



Ctev Clubfoot Should Be Treated Early To Avoid Complications Shvong
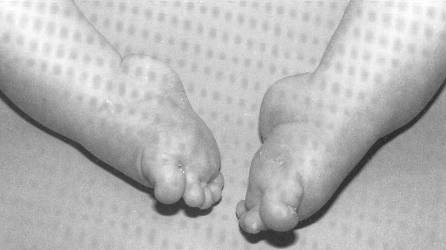


Clubfoot Congenital Equinovarus Cev Team Bone



Ctev Foot Anatomical Terms Of Motion
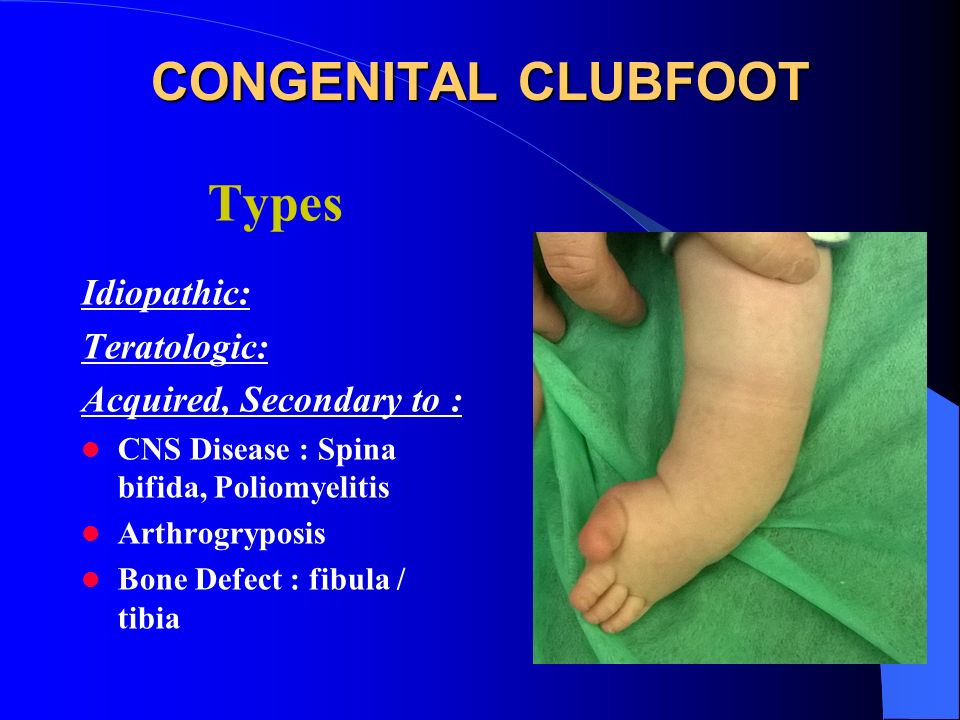


Congenital Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Ppt Video Online Download



4 1 Clubfoot Types Clubfoot Guide 123


Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets


Clubfoot Symptoms Stages Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis



The Newborn Foot American Family Physician



Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Merck Manuals Consumer Version


Clubfoot Flip Ebook Pages 1 Anyflip Anyflip



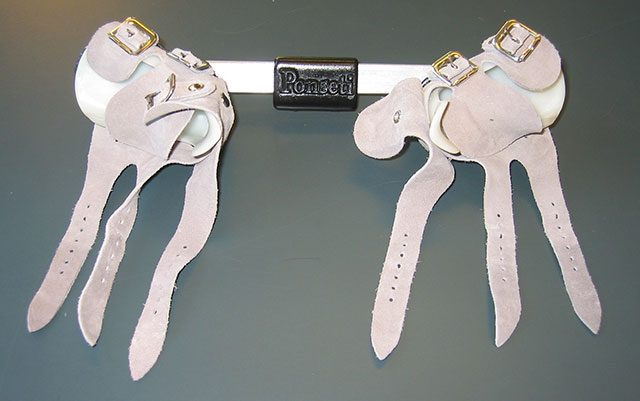
Clubfoot Treatment With A Boots And Bar Orthosis



Club Foot Symptoms And Treatment


Clubfoot Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials



Clubb Foot


Clubfoot Orthoinfo os


Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Drbond Happy Bonding
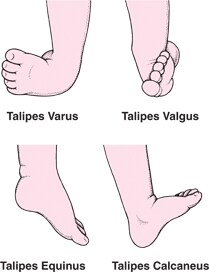


Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Medicine Com



Club Foot


Clubfoot What Is Clubfoot What Causes Clubfoot Who Gets Clubfoot What Are The Symptoms Of Clubfoot
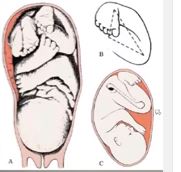


Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
/GettyImages-976611020-532e1800b14b4c89aec1f2f6a855f199.jpg)


Newborn Baby Foot Problems And Deformities
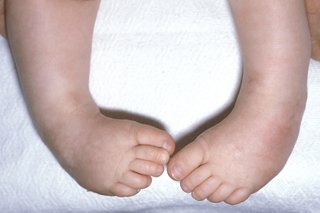


Club Foot Nhs
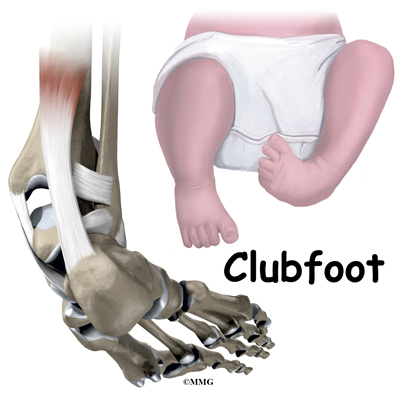


Clubfoot Eorthopod Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿